策略模式(Strategy) : 定义了一系列算法, 把这些算法封装起来, 算法和算法之间可以方便的替换, 属于对象行为模式, 它能够把复杂的同类型的不同逻辑区分开来, 让代码更清晰.
设计模式-概述
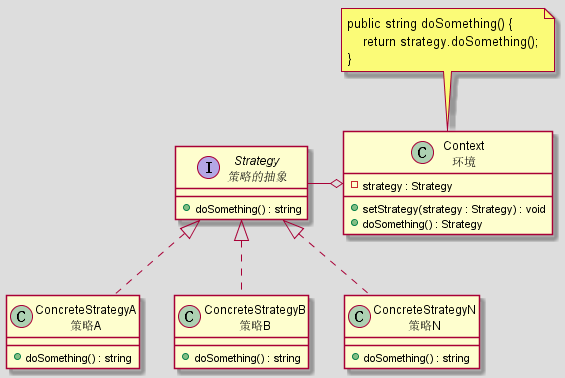
结构
策略模式有如下构成:
- strategy 策略的抽象
- ConcreteStrategy 策略的具体实现, 可以有多个
- Context 策略的执行环境
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| @startuml strategy-1
!include common.cuml
Interface(Strategy,"策略的抽象") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyA,"策略A") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyB,"策略B") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyN,"策略N") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(Context,"环境") {
- strategy : Strategy
+ setStrategy(strategy : Strategy) : void
+ doSomething() : Strategy
}
note as N1
public string doSomething() {
return strategy.doSomething();
}
end note
Strategy --left--o Context
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyA
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyB
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyN
N1 .. Context
@enduml
|
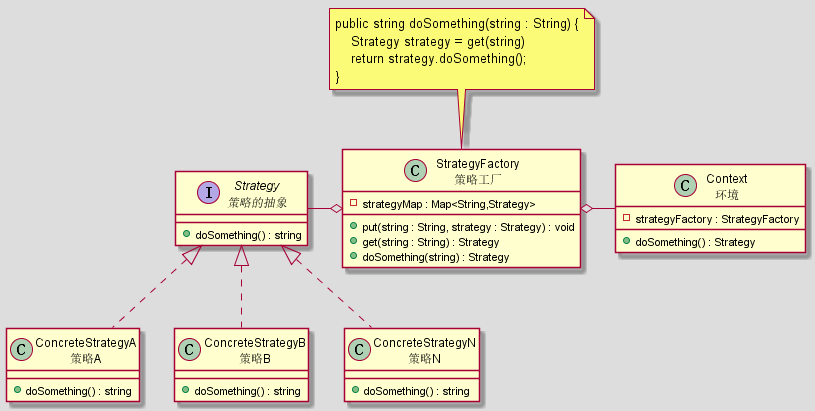
进阶版本
针对策略特别多的场景, 引进策略工厂来维护
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| @startuml strategy-2
!include common.cuml
Interface(Strategy,"策略的抽象") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyA,"策略A") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyB,"策略B") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(ConcreteStrategyN,"策略N") {
+ doSomething() : string
}
Class(StrategyFactory,"策略工厂") {
- strategyMap : Map<String,Strategy>
+ put(string : String, strategy : Strategy) : void
+ get(string : String) : Strategy
+ doSomething(string) : Strategy
}
Class(Context,"环境") {
- strategyFactory : StrategyFactory
+ doSomething() : Strategy
}
note as N1
public string doSomething(string : String) {
Strategy strategy = get(string)
return strategy.doSomething();
}
end note
Strategy --left--o StrategyFactory
Context --right--o StrategyFactory
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyA
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyB
Strategy <|.. ConcreteStrategyN
N1 .. StrategyFactory
@enduml
|
代码实现
- 有两个策略, 分别是:
- 通过名字分析出这个是啥东西
- 通过描述分析出这个是啥东西
- 先用名字分析出是什么并打印
- 后用描述分析出是什么并打印
可以看出, 对于新Strategy的增加, 该设计模式是开放的, 用户可以自行增加策略, 只要实现了Strategy接口.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context = new Context();
context.setStrategy(new StrategyA("西瓜"));
System.out.println(context.doSomething());
context.setStrategy(new StrategyB(Arrays.asList("圆的", "夏天")));
System.out.println(context.doSomething());
}
}
interface Strategy {
String doSomething();
}
class StrategyA implements Strategy {
private String name;
public StrategyA(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String doSomething() {
System.out.println("根据名字分析:" + name);
String result = name;
return "这个东西是个" + result;
}
}
class StrategyB implements Strategy {
private List<String> descriptions;
public StrategyB(List<String> description) {
this.descriptions = description;
}
@Override
public String doSomething() {
for (String s : descriptions) {
System.out.println("根据描述分析: " + s);
}
String result = "某某";
return "这个东西是个" + result;
}
}
class Context {
private Strategy strategy;
public Strategy getStrategy() {
return strategy;
}
public void setStrategy(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public String doSomething() {
return strategy.doSomething();
}
|
使用场景
策略模式有如下优点:
- 可以避免各种
if-else. 如果每一个分支都有很多内容, 可以封装这些不同的内容到不同的类中.
- 各种策略本身就是可拓展的, 可以用新的类包装它, 来做到更加复杂的策略.
- 策略模式对开闭原则完美支持, 增加新策略, 不用动旧策略.
- 策略和策略的使用实现了解耦, 分成了
Context和ConcreteStrategy.
有如下缺点:
- 策略如果很多, 不好维护.
- 每个策略如果内容很简单, 还不如写成
if-else的形式, 强行用策略模式反到增加了复杂度.
适用于
- 系统需要动态选择一个算法行为. 这样的行为有很多.
- 各个算法之间完全独立, 没有关联.
- 算法的内部逻辑一次实现, 改动比较小, 或者改动仅仅影响当前策略.
- 上层并不关心策略的内部具体实现. 仅需知道策略需要哪些信息, 传递进去即可.
具体应用
java.util.Comparator 接口是比较器的接口. 可以通过 Collections.sort(List,Comparator) 和 Arrays.sort(Object[],Comparator)来调用, Comparator 就充当了策略.- Spring Resource接口, 提供了不同类型资源的访问策略, 例如
ByteArrayResource, FileSystemResource 和 PathResource 等等.

